Wednesday, 29 April 2020
CLI aws error
I installed AWSCLI using pip install awscli command but still got this error. It got resolved after upgrading the aws with the command pip install --upgrade awscli
Thursday, 23 April 2020
Study Notes - DynamoDB 學習筆記
DynamoDB 設計理想源自於 Amazon 的論文: Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store, 2007 ,被稱為是 NoSQL 代表之作 。
這篇由 Werner Vogels (AWS CTO) 寫的 Blog: Amazon DynamoDB – a Fast and Scalable NoSQL Database Service Designed for Internet Scale Applications ,提到了 DynamoDB 背後設計的歷史、包含以前的 SimpleDB,文章提到幾個設計的重點:
- Fast (快)
- Managed (好)
- Scalable (好)
- Durable and Highly Available (好)
- Flexible (好)
- Low cost (便宜)
Anyway,以下整理的是 DynamoDB 的重要概念、背後運作的原理。圖文資料都出自官方文件:DynamoDB Developer Guide 。 (有點像在翻譯練習 XD)
核心元件 (Core Components)
經常會跟 MongoDB 比較,概念很類似:
- Tables:
- 類似於 RDBMS 的 Table.
- DynamoDB Table 是一個儲存集合單位。
- 相當於 MongoDB 的
Collection
- Items:
- 每個 Table 可以有多個 Items,相當於 RDBMS 的 Rows。
- 每個 Items 可包含多個 Attributes
- 相當於 MongoDB 的
Document
- Attributes:
- 每個 Items 由一個或多個 Attributes 組成
- Attribute 的資料型態有
- 建立 Attribute 時,注意保留字:Reserved Words
Primary Key
DynamoDB 支援兩種 Primary Keys:
Partition key:- 又叫 hash attribute ,指定某一個 attribute 當作 primary key (unique key),稱作
partition key,類似於 RDBMS 的 Unique Key. - DynamoDB 利用這個值透過內部的 hash function,然後依據 hash 過的值,決定資料要放在哪個實體的儲存體 (Storage)。這概念類似於 Sharding (分片) 的想法。
- 基本上,不會有重複的 hash value,也就是不會有重複的 partition key。
- 又叫 hash attribute ,指定某一個 attribute 當作 primary key (unique key),稱作
Partition key and sort key:- 使用兩個 attribute 的複合鍵 (composite key):
partition key+sort key, 或者稱為hash key+range key sort key又叫 range attribute- 如果 sort key 存在,那麼 partition key 可以重複
hash key + range key必須是唯一- 最常用的例子就是
unique key+date range這樣的組合。
- 使用兩個 attribute 的複合鍵 (composite key):
Secondary Indexes
一個 Table 除了 Primary Key,可以有一個或多個 Secondary Indexes,每個 Table 最多各五個 GSI 跟 LSI:
Global Secondary Indexes (GSI): 有自己的 Partition 和 RCU / WCULocal Secondary Indexes (LSI): 與 Table 共用 Partition 的 RCU / WCU
Data Type
Scalar Types (純量): number, string, binary, Boolean, and null.Document Types: list and map.Set Types: multiple scalar values, 包含 string set, number set, and binary set.
Read Consistency (讀取一致性模型)
DynamoDB 設計在每個 Region AZ 都可以快速的 Replica 資料,通常會在 1s 以內或更少。DynamoDB 支援兩種一致性模型:
Eventually Consistent Reads (最終一致性, ECR): 每秒可以讀 2 次, 每次 4KB 大小,所以可以讀取最大為 8KiBStrongly Consistent Reads (強制一致性, SCR): 每秒可以讀 1 次, 每次 4KB 大小。
這兩個的差異:ECR 不會反映最近完成的寫入操作結果,而 SCR 則一定會反應最近寫入的結果。
因為 DynamoDB 本身在 AWS Region 裡都是跨 AZ,每個 Table 都會存在各地三個副本 (Reclica)。
透過 API 指定用什麼方式,預設是 Eventually Consistent Reads,以下是 Node.js 的範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | var params = { TableName: 'STRING_VALUE', /* required */ ConsistentRead: true || false, // ECR or SCR }; dynamodb.getItem(params, function(err, data) { if (err) console.log(err, err.stack); // an error occurred else console.log(data); // successful response }); |
更多最終一致性模型,參閱 Eventually Consistent 與 Dynamo NWR 模型。
Global Tables
— 待整理 —
Read/Write Capacity Mode
Provisioned Mode
DynamoDB 每個 Table 都有讀寫能力單元 (Capacity Units) 的設定,稱作
Read Capacity Units (RCU)、Write Capacity Units (WCU).Read Capacity Units (RCU): 每次讀取單位為4K- Strongly Consistent Reads 每秒讀一次
- Eventually Consistent Reads 每秒讀兩次,也就是每秒 8KB
- 如果讀寫大小超過
4KB,那麼就會需要額外的 RCU
Write Capacity Units (WCU): 每次寫入單位為1KB,超過大小就會額外消耗 WCUSecondary Indexes會另外消耗 Capacity Units,有獨立的 RCU / WCU
RCU / WCU 這兩個值會影響效能,也會依據需求收費。
DynamoDB 讀寫的 API:
- Read:
- GetItem: 一次取回一個 Item
- BatchGetItem: 一次操作最多取回 100 Items
- Write:
- PutItem / UpdateItem / DeleteItem: 單一個 Item 操作
- BatchWriteItem: 一次操作,最多 Put / Delete 25 Items
另外,Provisioned Capacity 可以:
- 買 Reserved Capacity。
- Auto Scaling
- On-demand (建議)
On-Demand Mode
以下情境適合使用 On-Demand Mode:
- 新的 Table,但無法知道需要多少 Read / Write Capacity
- 有無法預期的請求流量
- 成本考量,期望用多少,付多少。 (不養機器的概念)
不過這種概念就是把使用的狀況,返回給使用者自行決定,換言之,如果沒有了解 RCU / WCU 的基礎概念,沒有良好的設計,屆時會反映在成本上,而不只是方便維運。
Guidelines for Working with Tables
Partition Behavior of Table
一個 partition 最多提供
3000 RCU / 1000 WCU。建立 Table 時,如果指定 1000 RCU / 500 WCU,那麼需要的 Partition 計算公式如下:Total partitions for desired performance = (Desired RCU / 3000 RCU) + (Desired WCU / 1000 WCU)
例如:1000 RCU, 500 WCU 需要幾個 Partition?
( 1,000 / 3,000 ) + ( 500 / 1,000 ) = 0.8333 --> 1
所以一個 partition 可以滿足上述的需求。如果 RCU / WCU = 1000,那麼需要的 partition:
( 1,000 / 3,000 ) + ( 1,000 / 1,000 ) = 1.333 --> 2
Partition Split
Partition Split 代表著拆分不同的區塊,儲存資料,每個 Partition 有其基本的讀寫能力與容量。一個 partition 可以儲存 10GiB 的資料,加上 RCU / WCU 的計算,所以以下兩個條件會發生 partition split:- 增加 capacity throughput
- 需要增加 storage 空間
Increased Provisioned Throughput Settings
建立一個 Table ,然後有 5,000 RCU、2,000 WCU,那麼初始的時候就會有 4 個 Partitions,計算公式如下:
( 5000 / 3,000 ) + ( 2,000 / 1,000 ) = 3.6667 --> 4
4 個 partition 將會被配份使用 1,250 RCU (5000/4)、500 WCU (2000/4)。
如果使用者把 RCU 調整成 8,000,那麼既有的四個 partition 就無法滿足需求,DynamoDB 會自動加倍 partition,變成 8 partitions。如下圖:
最後再把資料平均分配到新的 partition。而每個 partition 的 RCU / WCU 會變成:
- RCU: 8000 / 8 = 1000
- WCU: 2000 / 8 = 250
Increased Storage Requirements
當資料量超過一個 partition 大小 10GB 的時候,就會自動長出新的。
上一個例子最後有 8 partitions,如果其中一個超過 10GB
Use Burst Capacity Sparingly
因為每個 partition 都有一定的 RCU / WCU,所以也就變成每個 Table 不管使用者要多少,實際上,都會有 buffer,所以如果有瞬間量的需求 (bursts 爆炸),實際上是可以撐一下的。
DynamoDB 保留了五分鐘的 burst 給 RCU / WCU。在這段時間的 R/W 動作,可以非常快速地被消化,基本上會比定義的還要快。
但是不要把 burst 的 RCU / WCU 當成設計的一部份,因為 DynamoDB 會預先使用這些 Capacity 作維護任務。
未來 burst 可能可以讓使用者自行設定。
Cache Popular Items
AWS 官方建議,如果有一些資料存取比較頻繁,建議使用
In Memory 的方式,像是 ElasticCache,或者 DAX。Limitation
Capacity Unit Sizes 是固定的值,讀 (RCU) 跟寫 (WCU) 都有預設值。而每個 AWS Account / Per Region 也都有一些上限,使用時要注意這些限制。以下資料整理自 Limits in DynamoDB
Capacity Unit Sizes:- RCU: 強一致性 (strongly consistent) 讀取,每秒 4KBytes、最終一致性 (eventually consistent) 則是 8KBytes 每秒.
- WCU: 每秒寫入 1KByte.
- Limit by Table and Account, 大部分的 Region 如下:
- Per table – 40,000 RCU, 40,000 WCU
- Per account – 80,000 RCU, and 80,000 WCU
40,000 RCU = 160MBytes, or 320MBytes
Development with DynamoDB
local development using docker
- DynamoDB 本身都是透過 Web Service 存取,所以沒有 RDBMS
Connection的概念,所以也不會有Connection Pool的問題。 - 2018 年開始提供了 docker image 給開發者使用:
docker run -p 8000:8000 amazon/dynamodb-local
- AWS 提供 DynamoDB local 版,需要 jre6 以上,使用方式如下:
1 2 | wget http://dynamodb-local.s3-website-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/dynamodb_local_latest.tar.gz java -Djava.library.path=./DynamoDBLocal_lib -jar DynamoDBLocal.jar -sharedDb |
相關資料:
NoSQL Workbench Preview (updated: 2019/09/17)
AWS 總算提供了 NoSQL Workbench ,主要提供以下功能:
- Data Modeling
- Data Visualization
- Operation Building
目前還在 Preview 階段。
使用時機
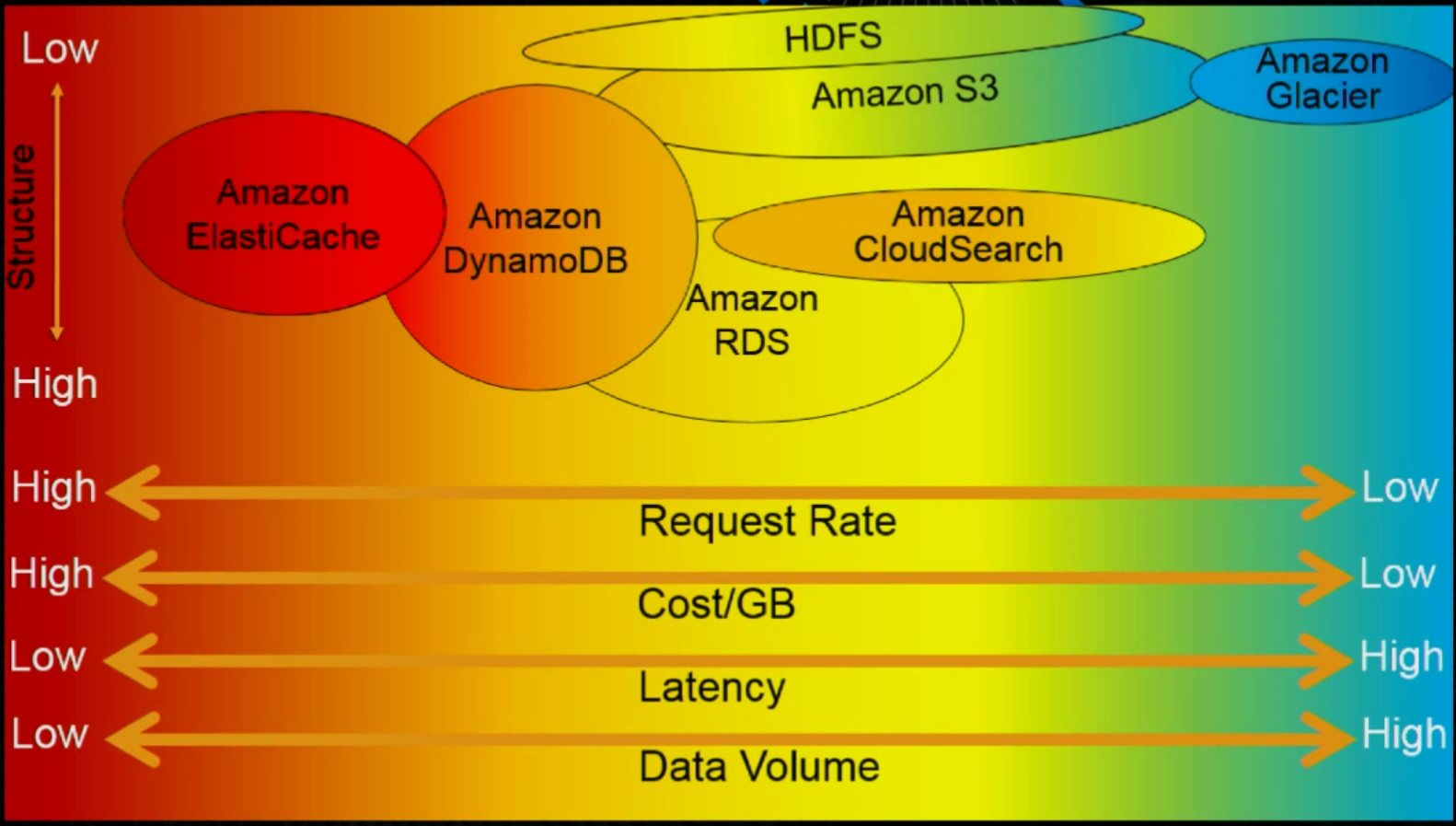
AWS 資料儲存有很多方式,不管是 S3 / RDS / DynamoDB / Glacier / ElasticCache / HDFS …. 在 AWS Whitepaper: Storage Options in the AWS Cloud 有很詳細的說明。
不過要快速瞭解的話,下面這張圖 (出自 AWS Summit Series 2016 - Big Data Architectural Patterns and Best Practices on AWS ) 是不錯的參考:
Design Patterns and Best Practice
AWS 官方整理了很多 DynamoDB 的 Design Patterns,很值得研究,整理如下。
- 2019/02/25: Design patterns for high-volume, time-series data in Amazon DynamoDB
- 2019/01/09: Resolve to follow Amazon DynamoDB best practices in 2019
- AWS re:Invent 2018: Advanced Design Patterns for DynamoDB (DAT401)
- Developer Guide: Best Practices for DynamoDB
from : https://rickhw.github.io/2016/08/17/AWS/Study-Notes-DynamoDB/
Amazon DynamoDB 筆記
DynamoDB 筆記
Amazon DynamoDB 頁面上的介紹:
Amazon DynamoDB is a fast and flexible NoSQL database service for all applications that need consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale.
資料型態的部份就跳過去了,這篇筆記的重點在於 index 的部份 (了解他如何 scale),尤其是對 RDBMS 有了解的人要如何從他所設計的架構理解 DynamoDB 的 index。
理論基礎是 Amazon 在 2007 年丟出的論文「Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store」,這篇論文影響了很多 open source project。
DynamoDB 的 index 有 Primary Key、Local Secondary Index Key (LSI) 以及 Global Index Key (GSI),在「DynamoDB Data Model」這篇有介紹。
這邊會拿 Blogger.com 這種多人的 Blog Hosting 當例子:
- 一個 user 可以有很多 blog。(table
user) - 一個 blog 可以有很多 post。(table
blog) - 一篇 post 可以有很多 comment。(table
post)
接下來就從 Primary Key 開始講。
Primary Key
Primary Key 保證唯一,這也是 DynamoDB 裡面可以達到 RDBMS 的 UNIQUE KEY 效果的最佳方式。
有兩種 Primary Key 的型態,一種叫做 Hash,另外一種叫做 Hash-Range。
兩種都需要指定某一個欄位是 Hash-based column,當作切割 (partition) 的依據。
第一種:Hash
以 table
user 來說,可以拿 user_id 來當作 Hash-based column,裡面有 blog_id 的 list。
以 table
blog 來說,可以拿 blog_id 來當作 Hash-based column,裡面有 post_id 的 list。
要注意的是,如果表格 PK 是 Hash,那麼就不能使用 LSI 與 GSI 了。只有另外一種型態 (Hash-Range) 才可以用 LSI 與 GSI。
相對的,Hash-based 的表格因為功能有限,效率通常很好 XDDD
第二種:Hash-Range
其實 Hash-Range 是一種別的 LSI,兩者最大的差異就是唯一性了。
另外一種 Primary Key 是 Hash-Range,他需要指定兩個欄位,其中其中 Hash 的欄位就如同上面的解釋,當作資料切割的依據。這邊的唯一性是指 (Hash column, Range column) 唯一,而非只有 Hash 唯一或是 Range 唯一。
剛剛說到需要指定的另外一個欄位,被稱為「Range」的原因是因為他可以有效率的以 hash + range query 查詢資料。
以 table
post 來說,可以拿 blog_id 當作 Hash-based column,再拿 post_id 當作 Range-based column,等下我們介紹 LSI 時再拿發表時間欄位排序。
同理,table
comment 可以拿 (post_id, commend_id) 當 PK。Query
PK 是 Hash 的當然就是指定 Hash-based column 直接查,條件只能是等號。
PK 是 Hash-Range 的除了可以用 Hash-based column 直接查 (還是只能用等號),另外可以用 Hash-based column + Range-based column 查。
以 SQL 的想法就像是
WHERE hash_col = 123 AND range_col BETWEEN (123, 456) 的感覺。反正 Hash-based column 一定要等號。
講到這邊,其實讀過上面提到的 Amazon 那篇論文應該就大概有感覺架構是怎麼搞的了:(這是推敲出來的,未必是實際架構)
- 用 Hash-based column 切 consistent hash ring 塞到不同機器上。PK 是 Hash 的到這邊就搞定了。
- PK 是 Hash-Range 的,還是照上面一條提到的,用 Hash-based column 切開,所以同樣的 Hash-based column 的資料都會塞到同一台機器上,於是就可以用有效率的 ordered tree 來存放 Range-based column 的資料,這樣就可以提供 query 了。
當然,考慮到需要實做 rebalance 機制以逐步擴充,這邊 consistent hash ring 的部份的作法可以更細膩,不過就不是這篇要談的重點了。
接下來要講重頭戲 LSI 與 GSI 了。
Local Secondary Index (LSI) 與 Global Secondary Index (GSI)
前面有提到 LSI 與 GSI 必須 PK 是 Hash-Range 的情況下能用,兩者都不強制唯一性。
LSI 與 GSI 都是 (Hash-column based, Range-column based) 的形式,差別在 LSI 的 Hash-column based column 必須跟 PK 的相同,GSI 的可以不用一樣。
所以對於 table
post 可以加一個 LSI (blog_id, post_datetime),就可以用 WHERE blog_id = 123 ORDER BY post_datetime DESC 拉出對應的文章了。
同理,table
comment 是 (post_id, comment_datetime)。from :
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)